I completely agree with Dr Ravi R paper on difficulties we face in treating children with rare disorders like Cystinosis and aHUS where noone seems to help these children with drugs and treatment and we struggle for it. Appreciate Dr Ravi's foundation on Cystinosis.
CYSTINOSIS a truly orphan disease - Report of the Cystinosis Foundation India | Rajan | Rare Diseases and Orphan Drugs http://rarejournal.org/rarejournal/article/view/81
Pediatric Nephrology India Blog
Friday, July 29, 2016
Cystinosis: Really an Orphan for Developing world
Wednesday, June 22, 2016
Lung ultrasound in Pediatric Fluid Overload
Lung ultrasound imaging may be superior to both echocardiographic methods and BIS in detecting volume overload in children with ESRD. Given the practicality and sensitivity of lung ultrasound imaging, this technique can be adopted alongside clinical examination and blood pressure in the routine assessment of fluid overload in children with ESRD.
An excellent study published in Pediatric Nephrology on the same
An excellent study published in Pediatric Nephrology on the same
Tuesday, June 21, 2016
Our review article published in "Pediatric Nephrology" journal !
Today we publish a much awaited review on "Nutritional Management of a Critically Ill child with Acute Kidney Injury" in the journal "Pediatric Nephrology". Thanks to Drs Rupesh Raina, Timothy Bunchman, Vijay Kher, Norma Maxvold and Pranaw Jha for all the help and support.
Link to the article here
Link to the article here
Tuesday, June 14, 2016
Importance of NINJA in Pediatric Nephrology
Current issue of Kidney International shows an excellent study from Dr Goldstein's group, Cincinatti. It talks on development and validation of a systematic screening program called Nephrotoxic Injury Negated by Just-in-time Action (NINJA), whereby children admitted to a noncritical care unit in our hospital deemed to be at high-risk of NTMx-AKI were recommended to have a daily serum creatinine (SCr) ordered to assess for AKI development.
By intensive monitoring, the exposure rate decreased by 38% (11.63–7.24 exposures/1000 patient days), and the AKI rate decreased by 64% (2.96–1.06 episodes/1000 patient days).
This figure shows improvement in exposure rates following NINJA.
By intensive monitoring, the exposure rate decreased by 38% (11.63–7.24 exposures/1000 patient days), and the AKI rate decreased by 64% (2.96–1.06 episodes/1000 patient days).
This figure shows improvement in exposure rates following NINJA.
Behavioural abnormalities and Mutations in children with CKD
We very commonly see children with CKD and ESRD with behavioural problems and autistic features and CAKUT. Current issue of Kidney International nicely shows the 17q12 deletions but not HNF1B intragenic mutations are associated with neurodevelopmental disorders.
Otherwise, Heterozygous mutations of the HNF1B gene are the commonest known monogenic cause of developmental kidney disease.
Otherwise, Heterozygous mutations of the HNF1B gene are the commonest known monogenic cause of developmental kidney disease.
Friday, May 13, 2016
Maternal NSAIDs and Renal Tubular Dysgenesis in neonates
Just saw a neonate whose mother took Nimesulide whole of her pregnancy for pain abdomen, and now the child is in renal failure. It is a difficult task counselling these parents with a neonate with renal failure.
Renal tubular dysgenesis (RTD) is characterized by absent or poorly developed proximal convoluted tubules.
The glomeruli appear numerous because of the absent proximal tubules in the cortex. Tubules are dilated, and the interstitium is expanded. RTD has been reported to occur as an inherited genetic defect. It has been recognized as a characteristic feature of angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor foetopathy. It has also been reported sporadically in association with exposure to other drugs, notably the non-selective, non-steroidal, antiinflammatory drugs
Image Source
Renal tubular dysgenesis (RTD) is characterized by absent or poorly developed proximal convoluted tubules.
The glomeruli appear numerous because of the absent proximal tubules in the cortex. Tubules are dilated, and the interstitium is expanded. RTD has been reported to occur as an inherited genetic defect. It has been recognized as a characteristic feature of angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor foetopathy. It has also been reported sporadically in association with exposure to other drugs, notably the non-selective, non-steroidal, antiinflammatory drugs
Image Source
Managing FSGS: New targets
Current Issue of Kidney International has an excellent review on potential targets for treating FSGS in future years. It is a must read for all researchers and scholars!
Controversies and Management of Cystinosis
Current Issue of Kidney International has an excellent paper on Cystinosis- from diagnosis to management, a must read for all pediatricians and pediatric nephrologists.
Nephropathic cystinosis is an autosomal recessive metabolic, lifelong disease characterized by lysosomal cystine accumulation throughout the body that commonly presents in infancy with a renal Fanconi syndrome and, if untreated, leads to end-stage kidney disease (ESKD) in the later childhood years.
Nephropathic cystinosis is an autosomal recessive metabolic, lifelong disease characterized by lysosomal cystine accumulation throughout the body that commonly presents in infancy with a renal Fanconi syndrome and, if untreated, leads to end-stage kidney disease (ESKD) in the later childhood years.
Sunday, May 8, 2016
CME Live: Session four
Curofy- India's largest community of verified doctors covered the CME-International Neonatal and Pediatric Nephrology Training Workshop live. This post was first published on the Curofy app.
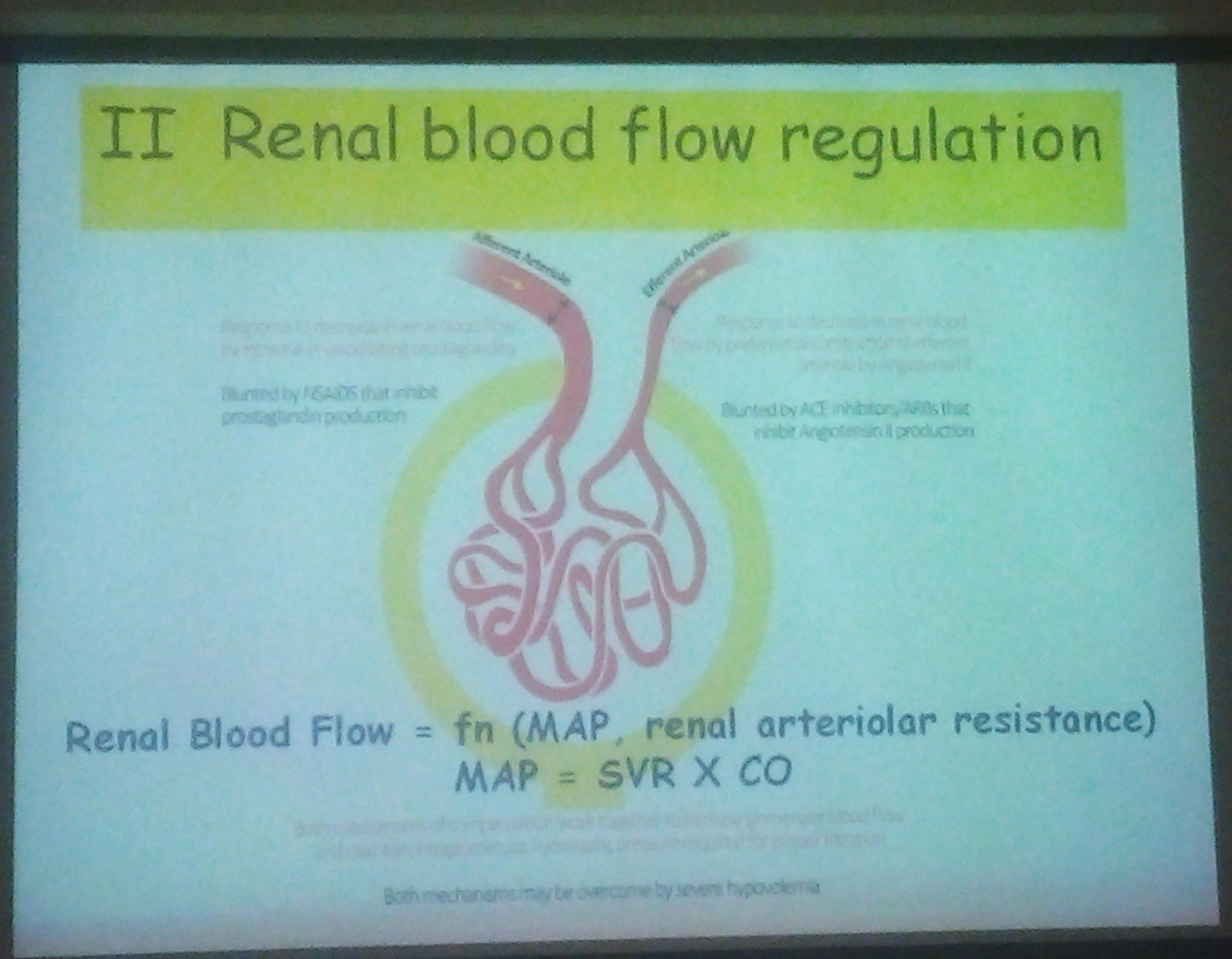
Glomerular function:
Kidney receives 15% of CO
Low systemic blood pressure
Increased vascular resistance
Renal blood flow more to inner cortex and medulla
GFR is 10-30 ml/min/1.73m2
Limited adaptive features to stress, sepsis, anorexia and exposure to nephrotoxic drugs are challenges in assessing renal function
Autoregulation:
Range of autoregulation set to lower perfusion pressure
Susceptible to Hypovolemic insult
Tubular function:
Total body water 75% of the weight
Shift of ECF into cells
Physiologic weight loss 10-15%
Low urine concentrating capacity
Dilution mechanism better than conc. capacity
Prone to dehydration
It maybe non oligouric despite poor renal function
Sodium balance:
Hyponatremia in preterms and rapidly growing LBW babies
Potassium levels of 6-6.5 is considered acceptable in term and preterm neonates
Acid base balance:
Suboptimal acid excretion
Lower serum bicarbonate levels are acceptable in preterm and term neonates
Disease states and drugs can accentuates metabolic acidisis.
Why did AK failure become AK injury, it should be AK dysfunction
Deficiency of AK*
Reduced GFR
Reduced urine output
Pre-renal causes:
Hypovolaemia
Non osmotic release of ADH
Renin/endocrine
Renin/paracrine
-Furosemide
does not lead to damage if reverses
Management:
Deal with reversible components
Improve renal perfusion
Sepsis
Surgery
Multiple organ failure
Furosemide if indicated
Obsessional fluid care
Blood results for fine tuning
When to dialyze?
Fluid is the key. If oligouric keep using conservative management until biochemistry is life threatening
Neonatal Renal Physiology
Dr Saroj patnaik
Dr Saroj patnaik
Glomerular function:
Kidney receives 15% of CO
Low systemic blood pressure
Increased vascular resistance
Renal blood flow more to inner cortex and medulla
GFR is 10-30 ml/min/1.73m2
Limited adaptive features to stress, sepsis, anorexia and exposure to nephrotoxic drugs are challenges in assessing renal function
Autoregulation:
Range of autoregulation set to lower perfusion pressure
Susceptible to Hypovolemic insult
Tubular function:
Total body water 75% of the weight
Shift of ECF into cells
Physiologic weight loss 10-15%
Low urine concentrating capacity
Dilution mechanism better than conc. capacity
Prone to dehydration
It maybe non oligouric despite poor renal function
Sodium balance:
Hyponatremia in preterms and rapidly growing LBW babies
Potassium levels of 6-6.5 is considered acceptable in term and preterm neonates
Acid base balance:
Suboptimal acid excretion
Lower serum bicarbonate levels are acceptable in preterm and term neonates
Disease states and drugs can accentuates metabolic acidisis.
Neonatal AKI
Dr Malcolm Coulthard
Dr Malcolm Coulthard
Why did AK failure become AK injury, it should be AK dysfunction
Deficiency of AK*
Reduced GFR
Reduced urine output
Pre-renal causes:
Hypovolaemia
Non osmotic release of ADH
Renin/endocrine
Renin/paracrine
-Furosemide
does not lead to damage if reverses
Management:
Deal with reversible components
Improve renal perfusion
Sepsis
Surgery
Multiple organ failure
Furosemide if indicated
Obsessional fluid care
Blood results for fine tuning
When to dialyze?
Fluid is the key. If oligouric keep using conservative management until biochemistry is life threatening
CME Live: Session Two
Curofy- India's largest community of verified doctors covered the CME-International Neonatal and Pediatric Nephrology Training Workshop live. This post was first published on the Curofy app.
Basics of RRT
Speaker: Dr. Pranaw Jha
Speaker: Dr. Pranaw Jha
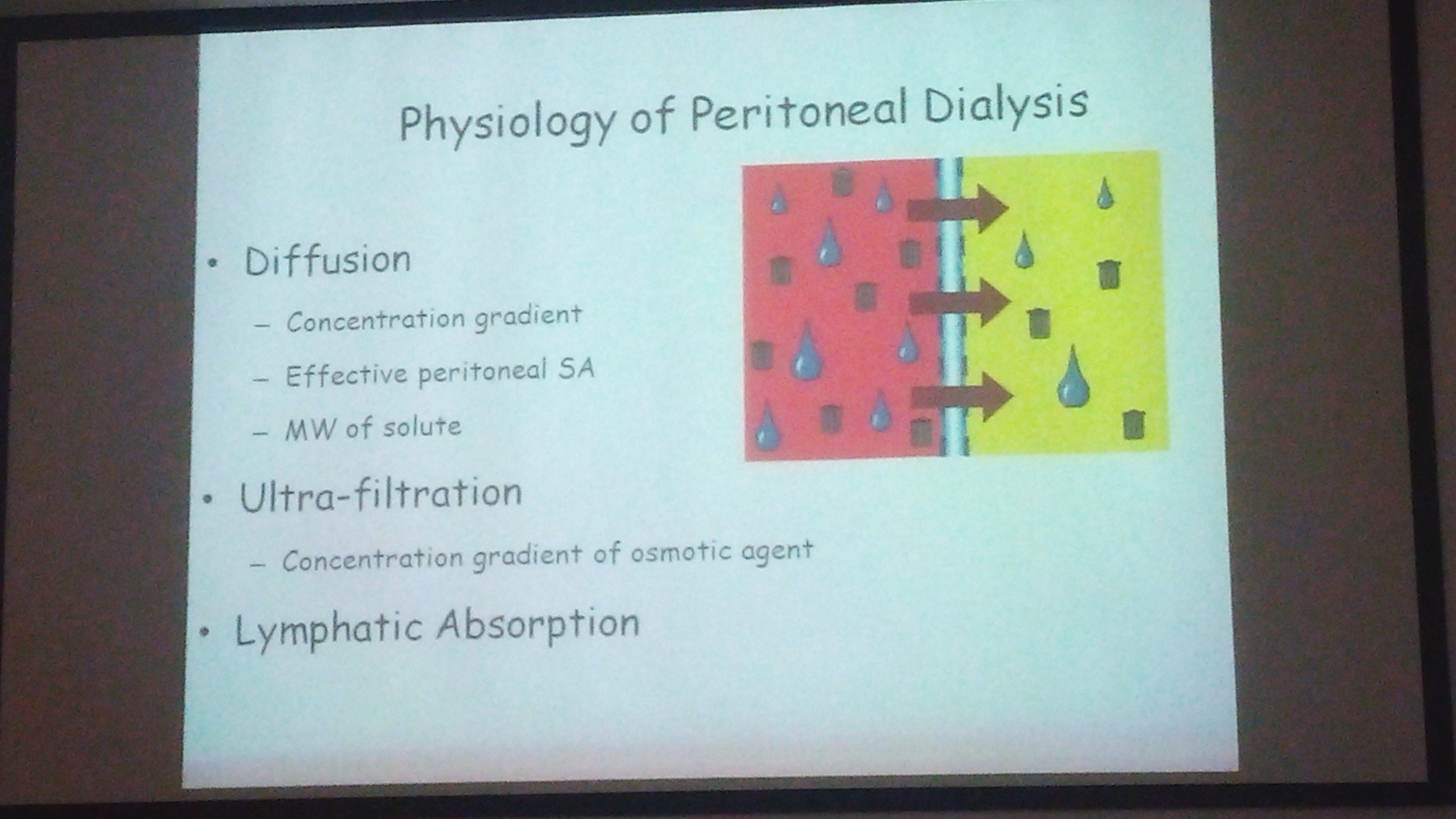
Dialysis process whereby soluble composition of a solution A is altered by exposing to solution B across a semipermeable membrane
-Need 2 solution- blood & dialysate
-Semi permeable membrane
Transport mechanisms:
Diffusion
Convection
Adsorption
Osmosis
Diffusion:
results in random molecular motion
inversly proportional to solute ssite
Convection:
Ultrafilteration
water driven across semipermeable membrane by hydrostatic/ osmotic force
solvent swept along with it, close to concentrated gradient- solvent drag
Convective methods:
Hemofilterationlarge amount of ultrafilteration coupled with replacement fluid infusion.
Hemodiafilteration: combined HD & HF
Dialysis Modality
Dr. Siddhartha Sethi
Dr. Siddhartha Sethi
Choice of modality
Peritoneal dialysis
intermittent hemodialysis
CRRT
PD is declining in the west, since expertise is increasing. CRRT is used
Modality of choice in India
less expertise in India
not insured in India
expensive
indication of CRRT
prevention of fluid overload
Acute peritoneal dialysis:
indication: Refractory volume overload
refract hyperkalemia
refract metabolic disease
uremia complication
dysnatemias in AKI
Apparatus:
PD catheter
three way connector
IV sets
PD fluid bags
Drain bag
Catheter:
Stiff catheter
two cuff tenckhoff's catheter
Cook's catheter
tenckhofs single cuff
soft thermal
Bicarbonate dialysis
Severe lactic acidosis or hepatic failure
asepsis required
1 hr exchange time
Ultra filtration
Not more than 5-10% weight loss should be targeted
Session length: Stiff catheter are 48-72 hr affair
anuria, hypercatabolism, nutritional support
Additives:
heparin, potassium, insulin
Disadvantage:
Slower concentration
lower URA clearance
lower ultra filtration
risks of peritonitis
Automated PD:
warm fluids, keeps track, less infection
Prescribing HD & Mathematics
Dr. Rupesh Raina
Dr. Rupesh Raina
Dialysis cannot clear solutes not present in intravascular space.
Diffusion:
Factors:
Conc. gradient(dC)
surface area(A)
diffusivity(KO)
sum of resistance(dx/KO)
concurrent flow
time
J=KOA x dC/dx
Solutes:
Low molecular weight- uo to 300 daltons
middle molecular weight- 300- 2000 daltons
large molecular weight- 5000- 1200 daltons
serum albumin-69 366 D
Hollow fiber dialyser;
Thousands of hollow capillary sizes fibers fixed in a polyurethane capsules.
blood flows through fibers, dialysate flows around fibers
Clearance: volume of blood cleared of solute per unit time.
( Refer pic)
KoA
Product of the overall mass transfer co efficient for a given solute x dialyser surface area
Ultrafilteration co efficient: ( KUf)
Volume of fluid transferred across the membrane per mmHg of pressure gradient
Low KUf denotes low permeability and low flux
high KUf denotes near complete permeability
High flux of dialyzers: KUf> 14ml/min/mmhg
Urea kinetic modeling:
Process to determine the amount of dialysis actually given
uses mathematical equation
( refer urea soup pic)
KT/V( Urea)
represnts fractional ura clearance
K= dialyzer clearance
T= time
V= volume of urea distribution
-0.5= uremic, death
-0.7= EEg abnormal
-1.0= short trm
-1.2-1.4= long term
->1.4= better outcome
Initial hemodynamic prescription concepts; Aim to prescribe a dose of dialysis to effect a desired result
Tubing: < 10 kg- neonatal tubing
10-20 kg- pediatric tubing
>20 kg adult tubing
SLED & CRRT
Dr. Timothy Buchman
Dr. Timothy Buchman
Continuous form of renal replacement therapy that allows for hemodynamic stability
SLED: Slow Low Efficiency Dialysis
Pediatric data for CRRT: optimal use in situation of hemodynamic compromise, Hypermetabolic state, sepsis
45% survival
Pediatric data SLED:
Heparin Anticoagulation
14 children in 16 sessions. less than 8 hours.
cheaper than CRRT
Advantages of CRRT:
Continuous in nature making decision making of medication, dosage and nutrition delivery easier.
Hemodynamically stable
Disadvantages, of CRRT:
greater need of utilization of resources
High pharmacy costs
Adv. of SLED
less resource utilization
less expensive
hemodialysis in morning and nocturnal SLED at night
Disadvantages of SLED
may cause hemodynamic compromise
intermittent
risk of over dialysis due to minimal dialysate flow of 6 ltrs per hour
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)